Embark on an in-depth exploration of advance study assignment the geometrical structure of molecules, a captivating journey that unveils the fundamental principles governing the shapes and properties of molecules. Delving into the realm of molecular geometry, this study assignment provides a comprehensive understanding of the VSEPR theory, hybridization, and the intricate relationship between electron pairs and molecular shape.
As we delve deeper into this fascinating topic, we will uncover the profound impact of molecular geometry on physical properties, chemical behavior, and its far-reaching applications in diverse fields such as medicine and materials science.
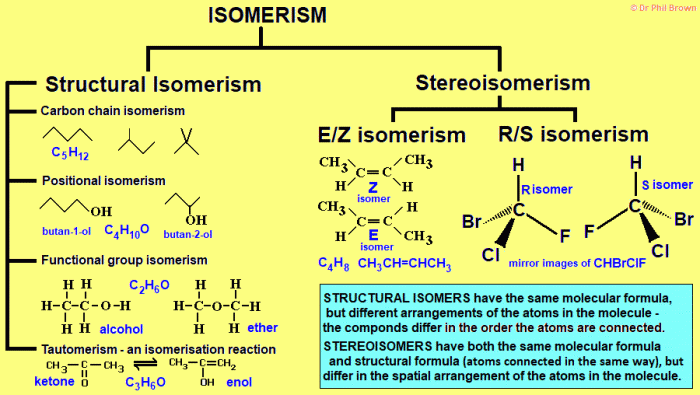
Introduction

Molecular geometry is the spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It plays a crucial role in determining the physical and chemical properties of a molecule.
The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory is a fundamental concept in molecular geometry. It states that electron pairs in a molecule repel each other, leading to the adoption of specific molecular shapes that minimize this repulsion.
Basic Principles of Molecular Geometry: Advance Study Assignment The Geometrical Structure Of Molecules
Shapes of Simple Molecules
The shapes of simple molecules are determined by the number of electron pairs around the central atom.
- Linear: 2 electron pairs
- Trigonal planar: 3 electron pairs
- Tetrahedral: 4 electron pairs
Electron Pairs and Molecular Shape
The number and type of electron pairs influence the molecular shape.
- Bonding electron pairs: Repel each other and determine the overall shape.
- Lone pairs: Repel bonding electron pairs more strongly, causing distortions in molecular shape.
Hybridization
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies. This concept helps explain the geometries of molecules with multiple bonds.
Advanced Concepts in Molecular Geometry
Resonance
Resonance occurs when a molecule can be represented by multiple Lewis structures with different electron arrangements. This can lead to changes in molecular geometry.
Geometry of Molecules with Lone Pairs
Lone pairs occupy more space than bonding electron pairs, influencing the molecular geometry.
- Lone pairs on central atom: Repel bonding electron pairs, causing distortions in shape.
- Lone pairs on terminal atoms: Have less impact on molecular shape.
Geometry of Complex Molecules
The geometry of complex molecules, such as organic compounds, can be more complex and requires consideration of multiple factors.
Applications of Molecular Geometry
Physical Properties, Advance study assignment the geometrical structure of molecules
Molecular geometry affects physical properties such as polarity, melting point, and boiling point.
Predicting Chemical Behavior
The geometry of a molecule can provide insights into its chemical reactivity and reaction mechanisms.
Applications in Fields
Molecular geometry finds applications in various fields, including medicine (drug design) and materials science (polymer chemistry).
FAQ Compilation
What is molecular geometry?
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule, determining its shape and properties.
How does VSEPR theory explain molecular geometry?
VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory predicts molecular geometry based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom.
What is hybridization, and how does it affect molecular geometry?
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies, influencing the geometry of the molecule.
