How to calculate transformation efficiency of competent cells? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of transformation efficiency, providing a thorough understanding of its calculation, influencing factors, and optimization strategies.
This guide will equip readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to accurately determine transformation efficiency, a critical parameter in molecular biology and genetic engineering.
1. Transformation Efficiency Overview
Transformation efficiency measures the ability of a cell to take up and express foreign DNA. It is a crucial parameter in molecular biology and genetic engineering, influencing the success of various experimental procedures.
Factors affecting transformation efficiency include cell type, plasmid concentration, DNA quality, and transformation method.
Different Transformation Methods
- Chemical transformation (e.g., calcium chloride method)
- Electroporation
- Microinjection
- Gene gun bombardment
2. Calculating Transformation Efficiency
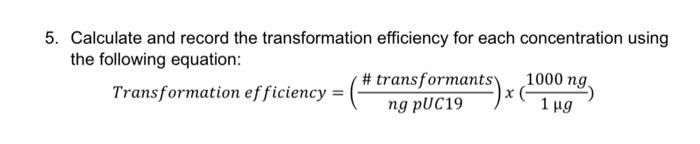
To calculate transformation efficiency, follow these steps:
- Count the number of transformants (colonies) on the selective plate.
- Count the total number of cells plated.
- Divide the number of transformants by the total number of cells plated.
- Multiply the result by 100 to express the efficiency as a percentage.
Formula for Transformation Efficiency
Transformation efficiency (%) = (Number of transformants / Total number of cells plated) x 100
Example Calculation
If 50 transformants are obtained from a plate with 1000 cells plated, the transformation efficiency would be:
Transformation efficiency = (50 / 1000) x 100 = 5%
3. Factors Affecting Transformation Efficiency
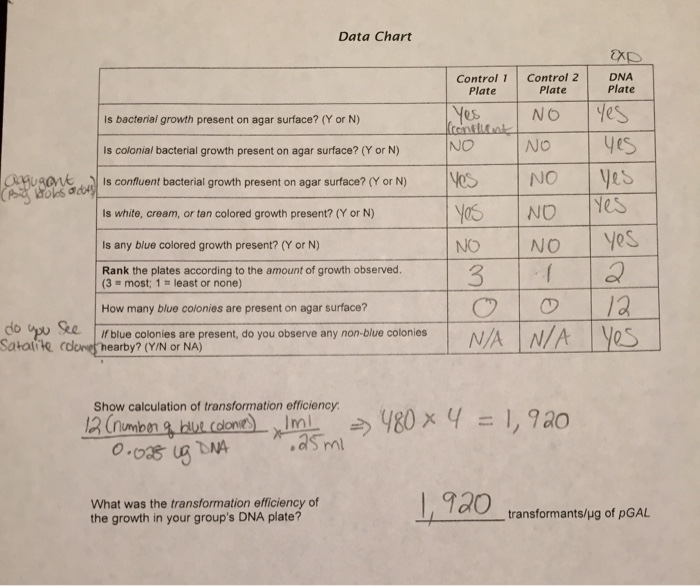
Cell Type
Different cell types have varying abilities to take up and express foreign DNA. Some cells, such as bacteria and yeast, are naturally competent and can readily take up DNA.
Plasmid Concentration
The concentration of the plasmid DNA used in transformation affects efficiency. Higher plasmid concentrations generally lead to increased transformation efficiency.
DNA Quality
The quality of the plasmid DNA is crucial. Damaged or degraded DNA will result in lower transformation efficiency.
4. Optimizing Transformation Efficiency

Cell Preparation, How to calculate transformation efficiency of competent cells
- Grow cells in optimal conditions.
- Use competent cells or induce competence.
- Remove inhibitors (e.g., antibiotics).
Plasmid Quality
- Prepare high-quality plasmid DNA.
- Use endotoxin-free plasmids.
- Linearize the plasmid for some methods (e.g., electroporation).
Electroporation Parameters
- Optimize voltage, capacitance, and pulse duration.
- Use appropriate buffers and cell suspensions.
- Follow manufacturer’s instructions.
5. Troubleshooting Transformation Efficiency Issues
Common Problems
- Low transformation efficiency
- No transformants
- Non-specific colonies
Troubleshooting Tips
- Check cell viability and competence.
- Optimize plasmid concentration and quality.
- Adjust electroporation parameters.
- Use positive and negative controls.
Interpreting Transformation Efficiency Results
Low transformation efficiency can indicate issues with cell preparation, plasmid quality, or transformation method. High transformation efficiency indicates successful DNA uptake and expression.
6. Applications of Transformation Efficiency: How To Calculate Transformation Efficiency Of Competent Cells

Transformation efficiency is crucial in molecular biology and genetic engineering:
- Creating genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
- Producing recombinant proteins
- Studying gene function and regulation
FAQ
What is transformation efficiency?
Transformation efficiency is a measure of the number of competent cells that successfully take up and express foreign DNA.
What factors influence transformation efficiency?
Factors that influence transformation efficiency include cell type, plasmid concentration, DNA quality, and electroporation parameters.
How can I optimize transformation efficiency?
To optimize transformation efficiency, optimize cell preparation, improve plasmid quality, and optimize electroporation parameters.